POLYVINYL CHLORIDE PVC & CPVC Key Facts
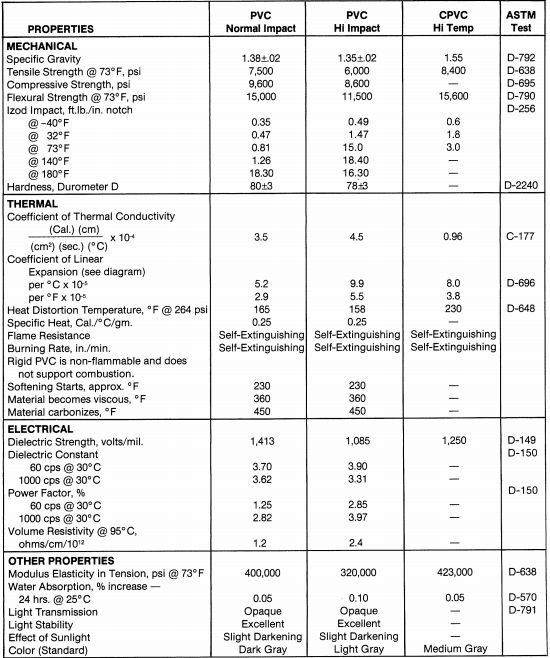
Polyvinyl Chloride is one of the most commonly used thermoplastics. Normally grey or white in color, PVC is readily associated with the plumbing industry. However, PVC is becoming widely accepted in industrial environments due to its wide range of properties.
PVC provides excellent weatherability and resistance to chemicals, moisture and abrasion.
The CPVC molecule has one more chlorine atom than the PVC (polyvinyl chloride) molecule. This extra chlorine is responsible for the material’s high temperature strength.
Key Benefits of PVC
• Chemical Resistance-PVC is inert to attack by strong acids, alkalies, alcohols, and many other chemicals.
• Strength-PVC provides both high tensile and high impact strength.
• Weather Resistance-PVC is not affected by direct sunlight, fungi or adverse soil conditions.
• Light Weight-PVC weighs 1/6th that of steel.
• Freedom from Toxicity, Odors and taste-PVC is approved by U.S.D.A., U.S. Navy and the National Sanitation Foundation.
• Non-Porous– PVC machines to close tolerances.
Applications of PVC
• Chemical – Oil refining, fertilizer manufacturing, photographic industry, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals.
• Food Processing-Beverage bottling, brewing, tobacco industry, water and sewage, dairy industry, distilling.
• Power and Electric-Atomic energy, coal mining, electric power industries, battery manufacturing.
• Industrial Plants-Aircraft, glass manufacturing, steel industry, aluminum industry, paper and pulp, textiles.